CONNECTIVE TISSUE: THE BUILDING BLOCK FOR STRUCTURE AND SUPPORT
Our connective tissue is an important part of the body. It supports and connects organs, vessels, and nerves, and also supplies them. Connective tissue is part of the supporting tissue and is important for the supply of nutrients and the removal of harmful substances. It also serves as filler material and stores water and fat.
In adults, the net-like collagenous tissue accounts for about 60 percent of body mass. This makes it the largest contiguous component of the body. The cells of the connective tissue are called fibroblasts. They produce collagen. This is important for the supporting and binding function of the fibers and for beautiful, firm skin.
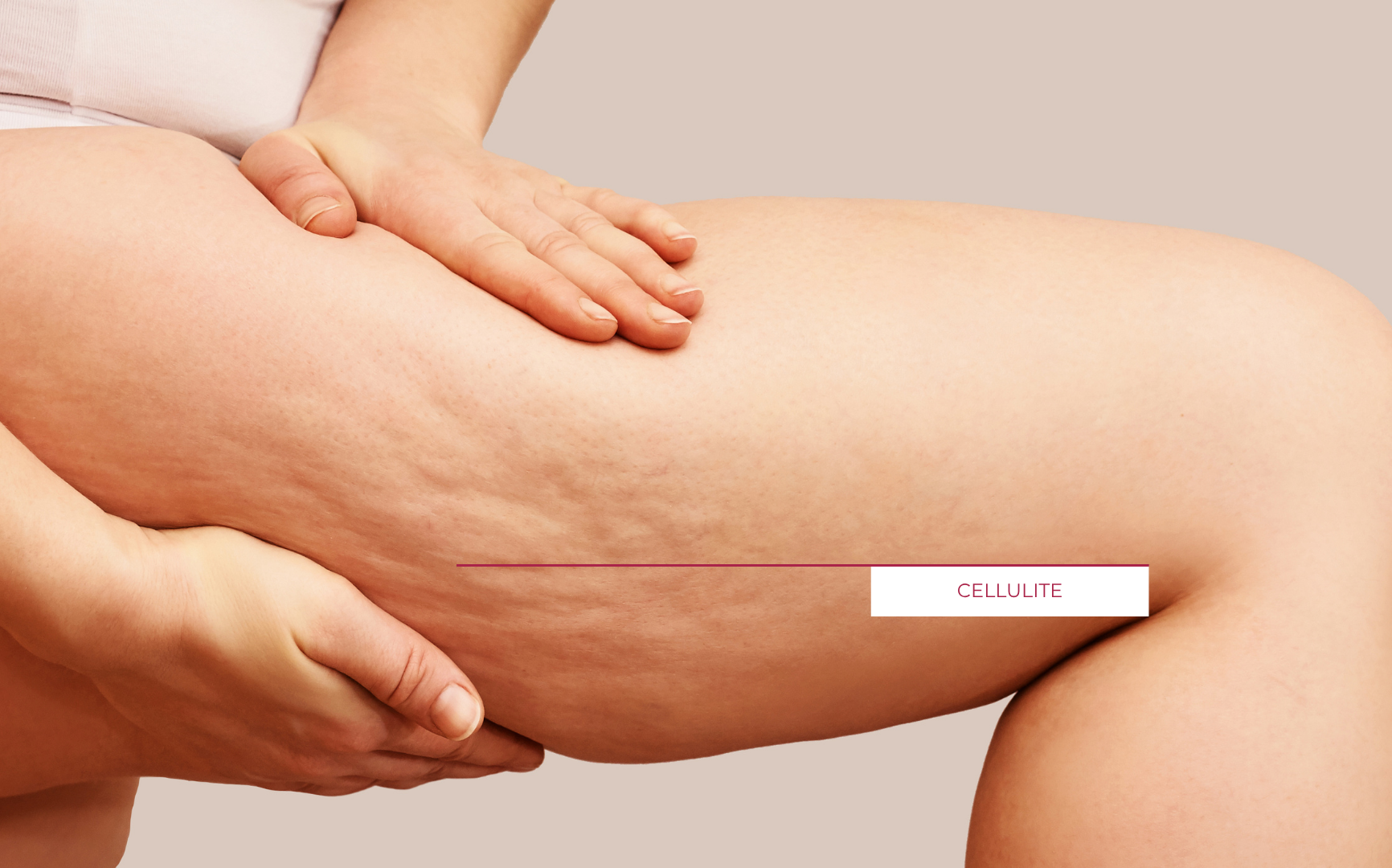
As can be seen in the illustration, the typical appearance of cellulite is visible on the skin’s surface. This is caused by changes in the connective tissue and the underlying fat layer. Below, you can learn more about the causes and characteristics of cellulite.
Why does connective tissue weaken with age?
Our skin consists of 80 percent collagen. This structural protein ensures skin density and smoothness. From the age of 25, the body’s own collagen production slows down. The collagen structure in the middle layer of the skin breaks down. This leads to the first wrinkles and reduced smoothness. At the same time, larger fat cell clusters form in the lower layers of the skin.
Connective tissue becomes increasingly weaker with age. Fat deposits can no longer be retained. They bulge outwards, resulting in the typical cellulite dimples. Due to their hormone balance and skin texture, women are more frequently affected by weak connective tissue than men. However, connective tissue can be positively influenced by various measures.
How can you STRENGTHEN YOUR CONNECTIVE TISSUE AND PREVENT CELLULITE?
| Measure | Effect |
|---|---|
| Vitamin C-rich diet | Citrus fruits, berries & peppers stimulate collagen synthesis and protect the fibers from UV damage; additionally, detox cures can prevent toxins from being stored in the tissue |
| Hydration & healthy fats | Adequate fluid intake and omega-3 fatty acids support cell metabolism and elastin architecture |
| Exercise & circulation | Regular exercise and alternating showers activate lymph flow and support cell regeneration |
| Targeted care & collagen supplements | Only the smallest peptides can penetrate deep into the dermis – products with vitamin C cofactors enhance bioavailability and stimulate fibroblast activity through sustainable peptide intake |